Domain-Domain Interactions
The database of 3D Interaction Domains (3did) is a collection of domain-domain interactions in proteins for which high-resolution three-dimensional structures are known. 3did exploits structural information to provide critical molecular details necessary for understanding how interactions occur. It also offers an overview of how similar in structure are interactions between different members of the same protein family. The database also contains GO-based functional annotations and interactions between yeast proteins from large-scale interaction discovery studies.
Domain-Motif Interactions
Many transient interactions are mediated by a short linear peptide recognized by a globular domain, creating a relatively small contact interface. We developed a method to identify peptide-mediated interactions based on structural features, and derived consensus motifs for those with sufficient non-redundant information (Stein et al., PLoS Comp Biol 2010). Those instances where the motif is significantly enriched in model species interactomes are included in 3did.
Domain-based
To retrieve information on a domain, use the Domain query in the Search page. You can give the exact domain name, or just part of it. If no exact match is found, 3did will return a list of similar domain names. If only one domain matches your search you will be redirected directly to the corresponding Domain page.
Motif-based
To retrieve information on a specific linear motif, use the Motif query in the Search page. You can give the exact name of the motif, or just part of it. Please notice that every motif's name starts with the name of the domain it interacts with. If no exact match is found, 3did will return a list of similar motif names. If only one motif matches your search you will be redirected directly to the corresponding Motif page.
The 3D structures of domain-motifs interactions currently stored in 3did are automatically discovered using the protocol described in the following publication:
Stein & Aloy,
Novel
peptide-mediated interactions derived from high-resolution
3-dimensional structures
PLoS Comput Biol, 2010, 6(5), e1000789
[link]
Search for a specific PDB entry
Given a PDB code use the PDB query in the Search page, to visualize all the details related to that particular PDB entry in 3did.
GO-based
Enter a GO accession code in the corresponding search field in the Search page and you will get the list of all domains annotated with that GO term. Alternatively you can browse the GO hierarchy on the Browse page and click on a specific GO term to search 3did for all the domains annotated with that term.
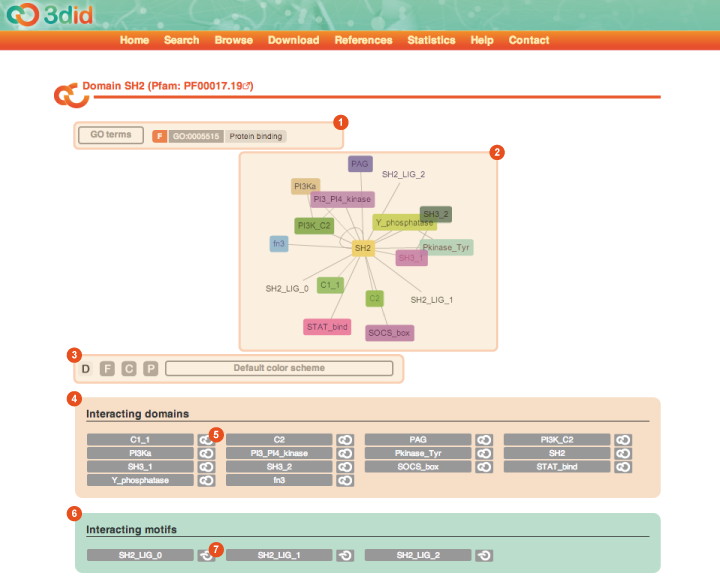
The Domain page reports information on a particular domain. The domain name, together with its Pfam ID, are reported in the title. Here you can see a picture of the Domain page for domain SH2, with a description of the different types of information that you can find on the page.
1 |
GO terms The list of GO terms associated with the domain. The colored box indicate the type of the GO term (F: Molecular function, C: Cellular component, P: Biological process). Clicking on the GO term ID you are brought directly to the corresponding page in AmiGO. |
2 |
Domain interaction graph It is an interactive CytoscapeWeb view of all the domains and motifs the domain under analysis interacts with. You can move the nodes in the network and click on them to be brought to a page reporting the details of the corresponding domain or motif. By clicking on one edge you are brought to the corresponding Interaction page. |
3 |
Color scheme By clicking on one of the buttons you can highlight the corresponding GO terms in the network view. |
4 |
Interacting domains This box reports the list of domains interacting with the domain under analysis. By clicking on one of the interaction buttons (5) you are brought directly to the corresponding Interaction page. |
6 |
Interacting motifs This box reports the list of motifs interacting with the domain under analysis. By clicking on one of the interaction buttons (7) you are brought directly to the corresponding Interaction page. |
If you scroll down the Domain page you can find two additional sections. One is dedicated to the global binding interfaces of the domain:
8 |
Interface visualization The interface visualization indicates which residues of a domain are used in an interaction. The interface residues are clustered for all cases of each interaction type, thus if more than one topology is shown, multiple interaction topologies can be observed in the 3D structures of this domain. In the domain view, global binding interfaces are shown, along with all binding partners that interact here. The bar height indicates how many partners actually use this residue in the interface. The visualization uses a "rainbow" colorscheme, i.e., N-terminal residues are in blue, then cyan, green, yellow, orange, and red at the C-terminus. |
9 |
Interacting domains and motifs By clicking on one of these buttons you are directly brought to the page of the corresponding interacting domain or motif. |
Finally, at the end of the Domain page you can find the list of PDB files in which you can find a structural template of the domain:
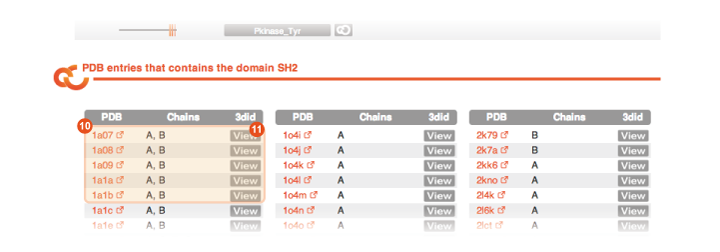
10 |
Table of PDB files Every line reports one PDB file in which there is a structural instance of the domain under analysis. |
11 |
View By clicking on the corresponding View button you are brought to the PDB page in 3didfor the corresponding PDB file. |
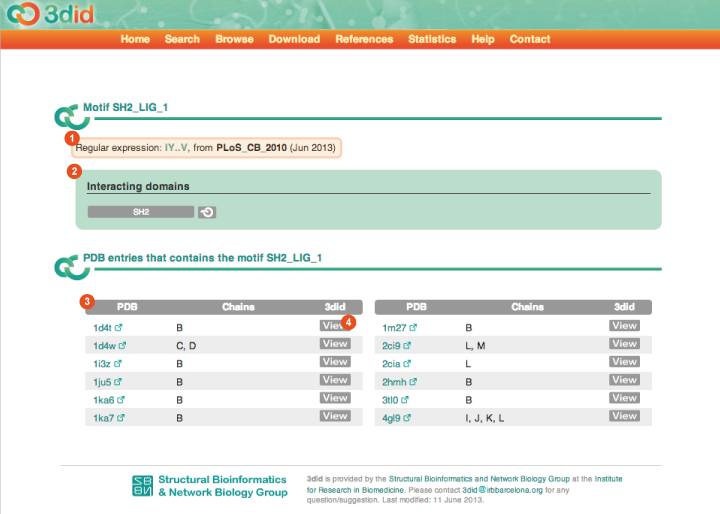
The Motif page reports information on a particular motif. Motifs in 3did are discovered with the method described in (Stein et al., PLoS Comp Biol 2010). The motif name is reported in the title. Here you can see a picture of the Motif page for motif SH2_LIG_1, with a description of the different types of information that you can find on the page.
1 |
Regular expression The regular expression derived for the motif under analysis and the source from which it is taken. Currently all the motifs in 3did are identified using the method described in (Stein et al., PLoS Comp Biol 2010). In the future we are planning to include motifs from databases like ELM, etc... |
2 |
Interacting domains The list of domains the motif interact with. For the moment each motif interacts with only one domain. In the future we plan to add ELM motifs that have been characterized in interaction to possibly multiple domains. |
3 |
Table of PDB files Every line reports one PDB file in which there is a structural instance of the motif under analysis in interaction with the corresponding domain. You can view the details of the PDB file by clicking on the View button (4). |
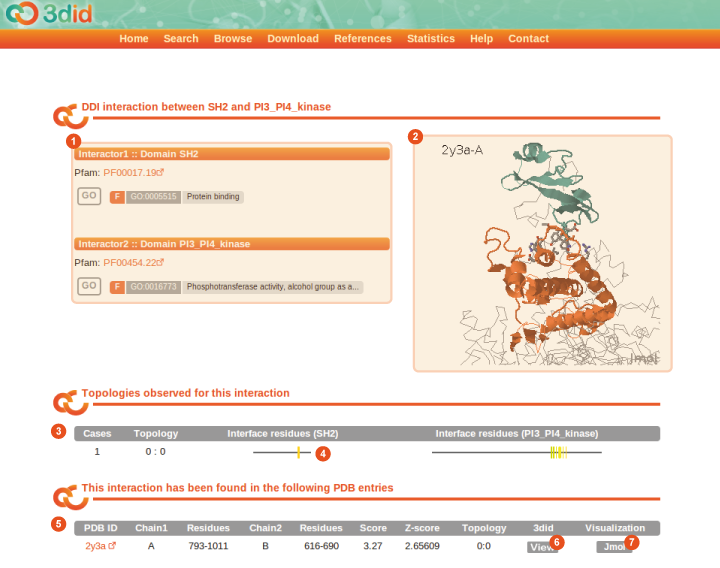
The Interaction page reports information on a particular domain-domain or domain-motif interaction. Here you can see a picture of the domain-domainInteraction page for the domain pair SH2-PI3_PI4_kinase, with a description of the different types of information that you can find on the page.
1 |
Interactors The two interactors (two domains or a domain and a motif) are listed here with some details. |
2 |
Jmol preview The right pane shows a preview of the interaction in the Jmol applet. You can explore the structure interactively with your mouse. |
3 |
Topologies Topologies observed for this interaction, via residues from both domains that form the interface, along with the number of cases in which we can observe this topology and a numeric identifier ("X : Y"). A graphical representation of the interacting residues (4) similar to the interface visualization, is also reported. |
5 |
PDB structures This table reports a list of all the instances of this particular interaction in the PDB. The PDB ID, starting and ending residues of the two domains (or the domain and the motif), the corresponding chains and the topology are reported for every instance. For domain-domain interactions the InterPreTS z-score is reported while for domain-motif interactions the "context residues" are reported. Furthermore, by clicking on the View button (6) you are brought to the PDB page summarizing the details of that particular PDB file while the Jmol button (7) changes the PDB structure visualized in the Jmol preview (2) at the top of the page. |
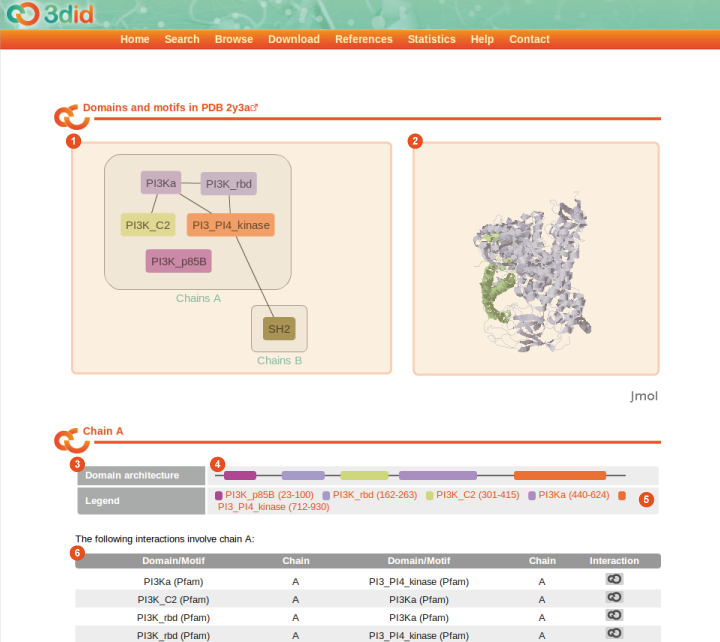
The PDB page reports information on a particular PDB file. For every chain it reports the domain architecture of the chain and the domain-domain as well as the domain-motif interactions. Here you can see a picture of the PDB page for the PDB ID 2y3a, with a description of the different types of information that you can find on the page.
1 |
PDB graph The PDB graph contains all chains of this PDB entry that are referenced in 3did plus their domains and motifs. Chains that contain the same domains are grouped into one block. Lines connecting the domains show both inter- and intrachain interactions. |
2 |
Jmol preview The right pane shows a preview of the PDB structure in the Jmol applet. You can explore the structure interactively with your mouse. |
3 |
Domain architecture For every chain in the PDB file, domains and motifs are displayed at their respective positions in the chain (4), linked to the corresponding 3did pages. A thin gray line indicates that there is no PfamA domain in this position. If there are overlapping domains or motifs, they are displayed in on an additional line below. The legend (5) gives detailed information about the domain position. Indices in the legend refer to the sequential numbering of residues inside the chain (starting from 0) and not on the residue numbers in the PDB file. |
6 |
Interactions in the chain This tables displays all the domain-domain and domain-motif interactions involving this chain. |
3did uses Jmol for the visualization of 3D structures. You need to install and enable Java as well as JavaScript for your browser in order to see the structures. Some helpful links and information:
- Java Downloads for All Operating Systems
- Enabling the Java plugin with Firefox
- Enabling JavaScript in Firefox
- How to activate JavaScript in your browser (IE, Firefox, Safari, Opera)
- In order to translate the molecule in space, you need to hold the Shift key pressed and double-click, then drag the cursor while holding the mouse button pressed down.
There are several way by which you can link to the contents of 3did:
- by domain name: https://3did.irbbarcelona.org/dispatch.php?type=domain&value=domName
- by Pfam access code: https://3did.irbbarcelona.org/dispatch.php?type=domain&value=accNum
- by motif name: https://3did.irbbarcelona.org/dispatch.php?type=motif&value=motifName